Understand Ectopic Pregnancy: Factors, Symptoms, and Options for Treatment
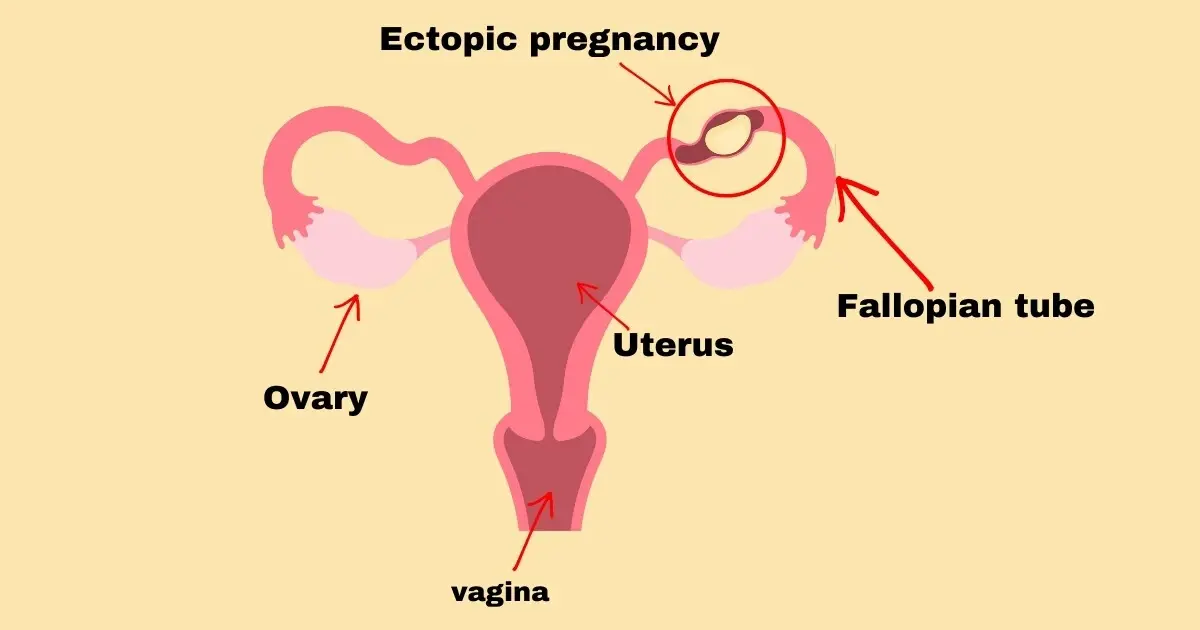
An ectopic pregnancy happens when a fertilized egg implants outside of the uterus, most typically in the fallopian tube. All births begin with an egg that has been fertilized. Normally, the egg that has been fertilized sticks to the lining of the uterus. However, in an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg implants and grows outside the uterus.
Most ectopic pregnancies occur in the fallopian tube because the fallopian tube plays a role in carrying eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. This kind of pregnancy is called a tubal pregnancy.
In rare cases, the fertilized egg implants in other parts of the body such as the ovary, cervix, or abdominal cavity. An ectopic pregnancy is not viable because the fertilized egg cannot survive outside the uterus.
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
The type of ectopic pregnancy that happens most often is tubal pregnancy. It occurs when a fertilized egg fails to travel to the uterus and implants somewhere else.
Some women get their fertilized egg stuck in the fallopian tube because it is broken or blocked. Abnormal development of the fertilized egg can also play a role in leading to an ectopic pregnancy.
Hormonal imbalances can also be a cause of this pregnancy. Any condition that slows down the movement of the fertilized egg from the ovary to the uterus can be a cause of ectopic pregnancy.
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy

This pregnancy can be difficult to detect in the early stages because the symptoms are similar to those of a normal pregnancy. If you decide to do a pregnancy test, the result is going to be positive.
As the fertilized egg continues to grow outside the uterus, the symptoms become more severe over time.
Some early symptoms and signs of an ectopic pregnancy include:
- Missing a period
- Feeling nauseous
- Tender and swollen breasts
- Fatigue and depression
- Increased urination
- Light vaginal bleeding
- Pelvic pain
- Sharp abdominal pain
- Dizziness
Severe Symptoms
Once the fertilized egg starts to grow in the fallopian tube, you will start to experience more severe symptoms, including:
- Heavy bleeding if the fallopian tube ruptures
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Rectal pain
- Pain in the shoulders and neck
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase a woman’s risk of ectopic pregnancy. Some of these include:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) – PID, a disease caused by an infection in the genital area, can increase the risk of that type of pregnancy. The infection usually spreads from the vagina to the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes.
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) – Infections from STDs such as Chlamydia or Gonorrhea can increase the risk.
- Ongoing Fertility Treatment – Women undergoing fertility treatments to stimulate ovulation have a higher risk.
- History of Ectopic Pregnancy – If you have already experienced an ectopic pregnancy, you are at a slightly higher risk of facing another such pregnancy.
- Contraceptive Device Failure – Some women can still become pregnant while using a coil or intrauterine device (IUD). In such cases, there is a significant risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Fallopian Tube Abnormality – If your fallopian tubes are swollen or damaged due to a previous infection or surgery, your chances of an ectopic pregnancy increase.
- Smoking – If you smoke, your risk of ectopic pregnancy is higher.
- Age – Women over the age of 35 have a higher risk.
Types of Ectopic Pregnancy
There are different types of ectopic pregnancy, classified based on the part of the body where the fertilized egg implants, as described below:
Tubal Pregnancy – This type of pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants in the fallopian tube is known as a tubal pregnancy. Most of this kind pregnancies are tubal pregnancies. A tubal pregnancy can occur in different locations within the fallopian tube:
- In 80% of cases, an ectopic pregnancy grows in the ampullary section.
- In about 12% of cases, the pregnancy grows in the isthmus of the fallopian tube.
- In about 5% of cases, a pregnancy grows at the fimbrial end.
- In about 2% of cases, the pregnancy occurs in the corneal and interstitial parts of the fallopian tube.
- Non-Tubal Ectopic Pregnancy – Although most ectopic pregnancies occur in the fallopian tube, about 2% of these pregnancies occur in other areas such as the ovary, cervix, or abdominal cavity.
- Heterotopic Pregnancy – This is a rare occurrence where two eggs are fertilized, one implants inside the uterus, and the other implants outside it. In such cases, the ectopic pregnancy is often diagnosed before the intrauterine pregnancy. In some cases, both pregnancies may cease, while in others, the intrauterine pregnancy may still be viable.
Treatment
An ectopic pregnancy, where the embryo develops, is not viable and cannot result in a full-term baby. Ectopic pregnancy treatment must be done to terminate the pregnancy before it causes significant harm to the woman.
These are the common treatment options available:
Expectant Management – If a woman shows little or no symptoms despite having an ectopic pregnancy, her doctor may closely monitor her for some time as there is a good chance the pregnancy will dissolve on its own. In expectant management, regular blood tests will be conducted to check the levels of HCG and other hormones in your blood. Some vaginal bleeding and mild abdominal pain are expected. If you experience more severe symptoms, you will be advised to consult with your doctor.
Medication – In cases where is detected early and expectant management is not deemed sufficient, you may be treated with medication. Doctors commonly prescribe Methotrexate, which prevents the pregnancy from further developing. This medication is given as an injection. Regular blood tests will be required to check if the treatment is working. You will be given another shot if the first one doesn’t work. Side effects of this medication include abdominal bloating, dizziness, and feeling unwell.
Surgery – Two types of laparoscopic surgery, salpingostomy and salpingectomy, are used for the treatment of some pregnancies. These procedures involve making a small incision near the naval area and using a laparoscope to view the tubal area. In a salpingostomy, only the ectopic pregnancy is removed, leaving the tube to heal on its own. In a salpingectomy, both the ectopic pregnancy and the tube are removed. The severity of the situation determines which of these procedures is used.
In Conclusion
A woman’s health could be seriously affected if it is not treated quickly. Some cases of it could be fatal. While the pregnancy can hurt a woman’s reproductive organs, it can be treated with prompt medical care and specific procedures. Some months after treatment for an ectopic pregnancy, the woman can get pregnant again. For the best treatment, come to Birla Fertility and IVF Clinic or call fertility specialists to set up a consultation.









